Chris Game
“Things from the past you’ll never see again”. I came across a listing of these recently, and they were – well, moderately interesting. More so, anyway, than the accompanying “trends that have unfortunately returned” – pleated skirts, corsets, and structured vests, whatever they were.
The never-see-agains included smoking adverts, bubblegum cigarettes, and rotary push lawnmowers – to which I might easily have added “The Barnet Graph of Doom” as at least a never-expected-to-see-again.
It was a visual aid devised a dozen or so years ago primarily for the councillors of the London Borough of Barnet. It would come, however, to be associated with/appropriated by Birmingham City Council, and something with which some INLOGOV colleagues were so taken that it was discussed and illustrated in these pages not once but repeatedly – by, inter alia, me in May 2012 and January 2013 and the Institute’s then Director and this blog’s progenitor, Catherine Staite, in December 2012 and October 2013. Indeed, as Catherine notes in that second blog, it at least part-prompted an INLOGOV ‘book’ or, more accurately, Discussion Paper.
Impactful at the time, then, but at least not prominently, I presumed, over the ensuing decade. Certainly I, though at best semi-detached from these matters nowadays, was genuinely surprised to be confronted by its reappearance in a recent Financial Times (indeed, its double reappearance). Somewhat less so that it was credited entirely to Birmingham City Council, with Barnet getting, as my mother would have said, nary a mention. Which justifies at least a brief résumé, and for more senior readers a bit of reminiscence.
Some 15 years or so ago the very Conservative Barnet LBC acquired the not entirely flattering moniker of ‘easyCouncil’ – that precise orthography/spelling, though frequently ignored in the media, being arguably the policy’s most appealing attribute. With its stray upper-case C intendedly referencing the easyJet business model that inspired the council’s almost boundless outsourcing drive for no-frills efficiency, it embraced pretty well all services, from reduced-size waste bins and privatised street cleaning to limited ‘personalised’ adult social care budgets.
Improved and cheaper services were obviously the aim, but senior officers foresaw that the sheer scale of demographic change – more children, more elderly – would in any foreseeable future take up an unmanageable proportion of the Council’s increasingly constricted budget. “No libraries, no parks, no leisure centres – not even bin collections”. Hence the original Barnet Graph of Doom. The one on the left of the illustration, that is – the other, pleasing if more alarmist one, being a public ‘reminder’ tweeted a few years later, just as the social services budget was seriously taking off as forecast.
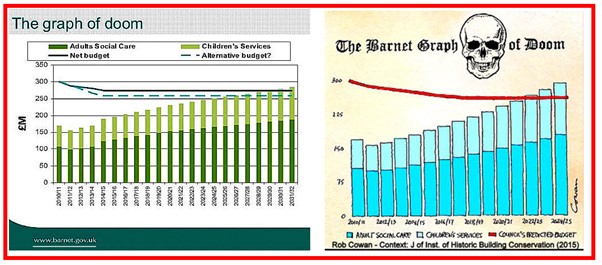
The Barnet graph, described at some length in my first blog and more summarily by the Guardian’s Public Services editor, David Brindle, started life as part of first a PowerPoint, later video, presentation used by the Council’s Chief Executive, Nick Walkley, to:
“focus the thoughts of colleagues and councillors … In five to seven years we get to the point where it starts to restrict our ability to do anything very much else. Over a 20-year period, unless there was really radical corrective action, adult social care and children’s services would need to take up the totality of our existing budget.”
The tone, as Brindle noted, was deliberately alarmist, with the policy making no provision, inter alia, for Barnet’s anticipated rise in income through regeneration schemes. As an illustrative device, though, it was hugely effective. It featured regularly in local government media, and also in presentations by the late Sir Bob Kerslake – then Permanent Secretary at the DCLG, and whose outstanding career in both central and local government was fulsomely recounted following his recent death.
Alarming, yes, but “Where are the jaws?”, I hear you ask – and, of course, there weren’t any, yet. They were Birmingham Council’s contribution when it took the idea over and “simplified/dramatised” it by, as Patrick Butler put it, again in The Guardian, projecting “a ‘budget pressures’ line rising steeply to the top right of the grid, and a ‘grant reductions’ line crashing to the bottom right.” It featured prominently as a ‘Jaws of Doom Graph’ in the council’s 2013 Budget Consultation document, and could indeed resemble, as Butler suggested, “a child’s depiction of a shark, or crocodile, about to bite its prey. Lunch, in this case, appears to be local government itself.”
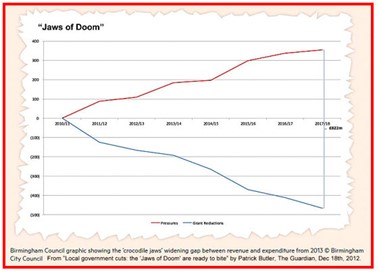
In my January 2013 blog I sought to address the question of whether the ‘doom-mongering’ was entirely fair: Were “Birmingham and urban councils generally, or Labour councils, or the country’s most deprived areas, being particularly harshly treated by the government’s grant funding cuts?”
Which, you’ll be relieved to learn, I’ll not be bothering you with here – not least because, as already noted, for the vast bulk of the past decade I’ve personally given these particular ‘Jaws of Doom’ and their graph scarcely a passing thought. Now, though, I wonder whether that’s simply another consequence of a retiree’s detachment from the daily concerns and parlance of local government personnel. Could it be that this is what today’s finance officers jaw about, as it were, down the pub of an evening?
For suddenly there it was, weeks before the journalistic ‘silly season’, and in ‘The Pink Un’ – no, not Norwich City FC’s newsletter, but the albeit self-styled “worldʼs leading global business publication”: “The Jaws of Doom” graph in its original glory, and not once but twice. First, in a kind of editorial intro by Associate Editor, Stephen Bush, commending to readers William Wallis’ “excellent piece … featuring this alarming chart [shown on the right below] about the … ‘jaws of doom’ facing local authorities”. And then Wallis’ article itself.

As you’d expect, it’s a good summary presentation – that I’d certainly be recommending to students, if I still had any – the thrust of which is that:
“for more than a decade, local authorities in England have been sacrificing services and staff to what they call “the jaws of doom” – a reference to a graphic produced by Birmingham city council to show worsening budgetary pressures, that resembled a crocodile’s mouth.
Between rising demand for social care and other essential services, and the dwindling funds councils have received to provide these, discretionary spending on everything from libraries to youth clubs has already been eaten up.
Although local authorities won a better than usual financial settlement for 2023-24, 9.4% up on the year before, inflation running at 8.7% is eroding any benefits.”
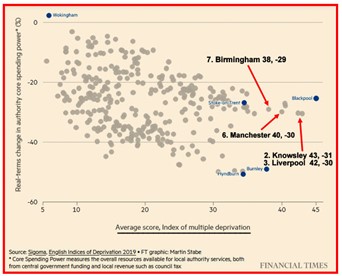
And, having already well exceeded a thousand words, that’s where I’ll stop … though not before sharing the interesting and, more importantly, interactive graph of Sigoma’s English Indices of Multiple Deprivation also included in Wallis’ article – not new, so doubtless familiar to some readers, but to me unfamiliar, informative (see added results), surprising in places, and, I felt, worth sharing. It made me (almost) sad not still to be lecturing and so able to play with it in public, as they say!
Chris Game is an INLOGOV Associate, and Visiting Professor at Kwansei Gakuin University, Osaka, Japan. He is joint-author (with Professor David Wilson) of the successive editions of Local Government in the United Kingdom, and a regular columnist for The Birmingham Post.