Sunday sees the 107th celebration of International Women’s Day (IWD), and for the 102nd year on March 8. It’s a longer history than is often supposed and, reflected in its still occasionally used Leninist title – International Working Women’s Day – a more socialist one. There were conspicuous exceptions, but the West as a whole didn’t really latch on to it until, following International Women’s Year in 1975, the UN proclaimed March 8 as the UN Day for Women’s Rights and International Peace and started increasingly to badge and orchestrate it.
That’s fine for those countries where it’s a public holiday, and for those who don’t celebrate Mother’s Day until early May. We, though, link that American creation to Mothering Sunday and the traditional Christian practice of visiting one’s mother church on the fourth Sunday in Lent (March 15 this year). There’s the risk, therefore, particularly when you throw in Valentine’s Day, of IWD morphing into another of those fluffy Spring days when women get a bit of a day off, like domestic servants of yore, and maybe a meal out.
With this in mind, I thought I’d do a quick check on who was doing what in furtherance of the cause. First – partly because they’re doing it literally as I’m typing (Thursday 5th a.m.) – MPs (well, some of them) are debating IWD-related matters in the Commons Chamber, thanks to an initiative from the Backbench Business Committee. Less fleetingly, the Commons Library has produced one of its invariably informative Briefing Notes on IWD itself and women’s equality generally, with some excellent data and references, including some examined later in this blog.
I then googled ‘IWD local government’ and immediately discovered that the first week in March was ‘Women in Local Councils Week’ – which sounded really admirable, until I realised it was in Northern Ireland; oh yes, and in 2012. Not this year apparently, and nothing either on the LGA website. So it was up to individual councils, of which the most prominent (if you live in Birmingham, you’d almost guess this) was Manchester.
You have to admire them: first Combined Authority, by a distance; centre of Chancellor George Osborne’s ‘Northern Powerhouse’; a specially tailored, top-of-the-range Devo Manc devolution package; and only last week a ground-breaking health and social care spending deal.
For IWD, the city council’s website has a classy-looking IWD page, its own IWD theme – ‘Breaking Through’ (snappier, certainly, than the UN’s ‘Empowering Women – Empowering Humanity: Picture It!’), its own annual IWD awards, plus a comprehensive listing of events.
But then, in addition, it has the chutzpah to claim itself as “the birthplace of women’s suffrage in the UK” – yes, of the whole suffrage movement, rather than, presumably, of the Women’s Social and Political Union at the Pankhursts’ Manchester home as late as 1903. Even the Manchester Suffrage Committee (1867) was preceded by Sheffield’s (1851); and what about Jeremy Bentham’s persistent advocacy, the 1832 and 1835 Acts that gave at least some women the actual right to vote, etc.? So, come off it, Manchester, don’t be greedy!
There was another surprise on the IWD website itself – that, of the 1,000+ IWD ‘events’ already registered, the UK will be contributing virtually twice the number of any other single country, the US included. Not all are happening this weekend; indeed, in the date-ordered listings the first actual IWD event doesn’t appear until page 17 – “A Gathering of Goddesses, celebrating ourselves, all women and Mother Earth” at The Hurlers stone circles in Cornwall.
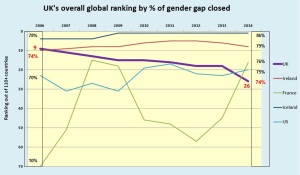
Sadly, one thing the Goddesses won’t be celebrating is this country’s narrowing gender gap – because it isn’t. Over the past decade, according to the best comparative data available, the UK’s overall gender gap hasn’t closed at all in absolute terms. Judged alongside some 120 other countries, the relative gap has widened, as it has on all major sub-indexes, on some of which it has widened absolutely.
The instrument that measures these things is the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap (GGG) Index, the 2014 report of which is its 9th annual edition.
Being an index, its principal interest is less in actual levels than in the gaps between men and women in four main categories (sub-indexes). Economic Participation and Opportunity records labour force participation rates, remuneration, and career advancement. Educational Attainment is about access to primary, secondary and tertiary education. Health and Survival combines sex ratios at birth – to capture internationally the phenomenon of ‘missing women’ – and healthy life expectancy. Political Empowerment compares the ratios of men and women in ministerial and parliamentary positions.
In all indexes, the highest possible score is 1 (equality) and the lowest is 0 (inequality), although in my own adaptations I prefer to lose the decimal points and percentagise the proportion of the possible 100% gender gap that’s been closed.
And the UK’s embarrassment, particularly on International Women’s Day, is that since 2006 our overall gender gap hasn’t closed by a single percentage point. In my graph, 74% of the gap was closed in 2006, and in 2014 it was still 74%, our ranking having dropped from 9th to 26th.
Meanwhile, all sorts of countries had overtaken us – not just the US and the volatile French, but from parts of the world one wouldn’t necessarily expect: Nicaragua (6th), Rwanda (7th), the Philippines (9th), Latvia (15th), Burundi (17th), Bulgaria (22nd), Slovenia (23rd) and Moldova (25th).
As already indicated, there’s not much to celebrate in any of the indexes, but naturally some make less embarrassing reading than others. In education, for example, we have a rare sub-index measure of more than 1.00 – a 1.36 female-to-male enrolment ratio in tertiary education – although it’s more than cancelled out by a 0.94 ratio for primary education.
Two sub-indexes are particularly gloomy. On none of the five Economic Participation measures is the UK ranked even as high as 45th, with ratios for career advancement of 0.52, for estimated earned income of 0.62, and wage equality for equal work of 0.69. And a Political Empowerment graph would look very similar to the overall one, the key difference being that the UK’s purple line of shame this time would signify an actual widening of the gender gap, with our ranking plummeting from 12th in 2006 to 33rd.
As we approach the election, our ratios of women in parliament and in ministerial positions are 0.29 and 0.19 respectively – compared, for instance, to Denmark 0.64, 0.83; Finland 0.74, 1.0; South Africa 0.81, 0.59; and Rwanda 1.0, 0.65. Of which the best that can be said is that at least the bar for the next lot to try to jump is set pretty low.
Chris Game is a Visiting Lecturer at INLOGOV interested in the politics of local government; local elections, electoral reform and other electoral behaviour; party politics; political leadership and management; member-officer relations; central-local relations; use of consumer and opinion research in local government; the modernisation agenda and the implementation of executive local government.