Chris Game
If, like Catherine Staite, you’re Director of an organisation and you risk entitling even an ironic blog: “Oh dear, … I’m wrong again!”, you must at least secretly hope that your underlings will be tripping over themselves to assure you that of course you’re not, either before or now.
If so, two months must seem a disconcertingly long wait, but my personal excuse is that I was waiting for a suitable peg on which to hang my grovel. Let us give thanks, then, for last week’s Conservative Party conference. Even before Chancellor George Osborne’s rabbit-out-of-hat business rates announcement, it had amply validated Catherine’s concern about the party political primacy of the Government’s whole devolution policy. And its timing also offered a useful opportunity for an update on devolution developments since my own last blog on the topic some of which, I wondered, might have prompted her to modify her earlier pessimism.
Recapping briefly: Catherine’s blog was about how neither of the two key opportunities for local government that she hoped for from the Government’s Devolution/Combined Authority agenda – the development of a sufficiently sizable scale of operation to enable the delivery of ‘big ticket change’ (her business jargon, I’m afraid), and “to improve collaboration by drawing in reluctant partners” – looked, at least in late July, like being significantly realised. Her vision of “a range of CAs operating at different scales and across varied geographies, receiving different devolution deals”, she felt, was proving to be self-delusion.
Her reasons included: George Osborne’s fixation with his Northern Powerhouse and metro mayors, and relative unconcern with counties and sub-regions; central government’s lack of either commitment or capacity to deliver effective devolution deals on any scale; and the sheer difficulty facing diverse and traditionally self-sufficient local authorities trying to develop convincing collaborative devolution bids within a ludicrously short time-frame.
The Treasury’s early September deadline was tough. Moreover, dictated by November’s Spending Review, it seemed to reinforce Labour sceptics’ suspicions of the Government’s whole strategy being more about the devolution of cuts than of powers, or, in the neat Newcastle version, passing the buck without the bucks. It was noticeable, however, that even some of those issuing such warnings, like Oldham Council leader Jim McMahon, were equally insistent that councils should still take “every bit of power from the Tories that we can. We have a responsibility to. It is our duty.”
For their part, ministers, or their civil servants, spent pre-conference week frantically negotiating, in order to maximize the political capital involved in such devolution giveaways by announcing at least one big one at the ideally located Manchester event. Cornwall’s (non-mayoral) settlement, rightly headline-making back in July, was politically now history, and it seemed the North East were being groomed as conference darlings. But then Sheffield City Region came up fast on the inside and breasted the tape on the Friday, before conference delegates had even convened.
Last year, the four South Yorkshire met boroughs comprising the CA were openly opposed to an elected mayor – and openly disappointed with the consequential paucity of their December ‘devo-lite’ deal. Since then, though, the addition of five Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire districts as non-constituent members, the General Election outcome, and the Cities & Local Government Devolution Bill had changed minds. Having accepted an elected mayor as the non-negotiable price of a worthwhile devolution deal, the region is for the moment head of the Manchester-chasing pack.
If the Bill weren’t sufficient confirmation that an elected mayor is indeed the price, regardless of anything electors themselves might have to say, this new agreement is peppered with references to the functions for which “the directly elected Mayor of the Sheffield City Region Combined Authority” will be responsible, and of course accountable. These include strategic planning and the region’s transport budget – with the delivery of a ‘smart ticketing’ service – while at CA level council leaders will get access to funding of £30 million a year for 30 years to boost local growth and invest in local manufacturing and innovation. From what I could tell, the Sheffield leaders got at least close to their bid document ‘offer’, which brings me to the second part of this blog.
Given the tight deadline and the known difficulty some aspiring CAs faced even agreeing their full memberships, the total of 38 “landmark devolution bids” seemed to impress others as well as, very obviously, the Government itself. The 38 included three from Scotland, one from Wales, and some constituting ‘expressions of interest’, rather than definite bids or, as DCLG Permanent Secretary Melanie Dawes put it, “offers that cannot be refused”. Several were manifestly eleventh-hour concoctions and/or overlapping, including no fewer than five from Yorkshire. So, while the modesty was disarming, it was hardly news when Grant Thornton’s timely survey found “around 1 in 5” of their interviewed local government leaders conceding that their devolution proposals were “fairly” or “very weak” (p.41). Even so, in this age of adjectival inflation, it seems all 38 must be referred to, irrespective of rationale or content, as ‘landmark’ proposals (LPs), just as Manchester’s deals are always ‘ground-breaking’, and all working class electors patronised as ‘hard-working families’.
These LPs were not public documents, and it was up to CAs themselves to release whatever details they wished. Any comprehensive comparison, therefore, has been impossible. Nevertheless, some attempted to do the best they could, perhaps most notably the Local Government Chronicle, whose analysis of 26 of the relatively more detailed English bids is summarized here in slightly amended and more easily comparable form.
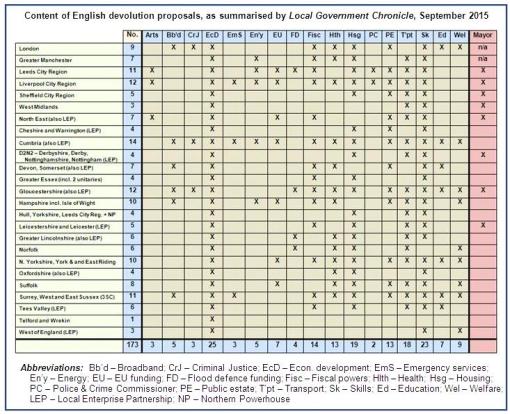
Bid proposals were coded into 18 policy areas, including ‘Fiscal powers’, plus the expressed readiness to consider an elected mayor. This latter was obviously unnecessary for Greater London and Greater Manchester, vital for the other metropolitan/city regional CAs – the more so after Osborne’s announcement that they alone will be able to raise business rates and levy a dedicated infrastructure tax – but interesting too in the bids involving counties.
Catherine referred somewhat sceptically to what Treasury officials reportedly envisaged as an at least three-county ‘East Midlands Powerhouse’. In the end, Derbyshire and Nottinghamshire agreed to submit a joint 19-authority D2N2 bid based on their two-county LEP, and there is talk, though not in the bid document itself, of an elected CA mayor. However, Leicestershire stuck with its single-county, but also LEP-based, bid, and, perhaps predictably, Leicester City mayor, Sir Peter Soulsby, has advised against another for the CA.
Whether these and the other county- and county/unitary-based bids will be judged to have, in Catherine’s phrase, “ticked all the boxes”, or at least a sufficient number of them, remains to be seen. Both East Midlands documents, and particularly the former, seem to me to constitute substantial and substantiated ‘offers’, the more persuasive in their having clearly emanated from directly relevant LEP and SEP (Strategic Economic Plan, not Someone Else’s Problem) experience and the partnership working involved, and the same could reasonably be expected of other such bids.
Moreover, even if boxes do remain unticked – and here I think Catherine may have been wrong – the signs are that it’s NOT “too late now”, particularly for these acknowledgedly more difficult multi- and cross-county arrangements.
Anyway, it’s the number, composition and comprehensiveness of some of these county- and county/unitary-based bids that I thought might possibly have prompted Catherine to wonder if she hadn’t slightly rushed to judgement and written off her hopes over-hastily. So I tried categorizing the 28 English non-city region bids (all those on the DCLG list, including Cornwall, not just those in the LGC list). It was obviously based in some cases on minimal knowledge and arbitrary judgements – particularly where whole-county LEPs are involved – but it provided a very rough statistical confirmation of what Catherine feared and what in the circumstances was only to be expected: that the bulk and probably a majority of these non-metropolitan bids – 15 of the 28, by my reckoning – would come from single counties.
The explanations will vary, but many will centre on the sheer shortage of time. Some took seriously ministers’ message about 5 September being the deadline for councils wanting to develop plans based on an existing or fairly solidly agreed Combined Authority with an elected mayor. Most counties, even more than most urban authorities, don’t want mayors, so why rush? But then over the summer the ministerial line changed to one of trying to drum up as many bids, or even expressions of interest, as possible – too late, though, for most counties, even if they’d wished, to respond other than individually.
Given a more generous time frame, and taking account of reported earlier discussions, it seems likely that at least some of, say, Norfolk and Suffolk, Oxfordshire, Buckinghamshire and Northamptonshire, Worcestershire and Herefordshire, Wiltshire (and Swindon), might have followed the D2N2 route and produced the joint, rather than individual authority, bids that the Treasury apparently favours. Which suggests that some may yet do so, and personally I’m particularly hoping the Oxon/Bucks/Northants combo progresses beyond its ‘England’s Economic Heartland’ transport alliance, thereby enabling me to note their questionable grasp of anatomy, with Bucks certainly appearing considerably closer to Gall-bladder-land.
Other existing multi-county bids, in addition to D2N2, include Surrey, West and East Sussex and Heart of the South West (aka Devon and Somerset), plus four that I categorized as primarily LEP-based: Cheshire and Warrington, the North East, Tees Valley, and West of England.
This left me with a motley group of 6, comprising Swindon, which may at some point resolve its ‘misunderstanding’ with LEP partners Wiltshire, Telford & Wrekin, which has since applied to become a non-constituent member of the West Midlands CA, and the shambles of Yorkshire, which would take a substantial blog on its own.
This blog, already over-long, I’ll bring to a close with two very brief conclusions. One, to date, both the Chancellor’s business rate plans and his devolution deals balance too calculatedly their freedoms and checks to constitute, outside the heady excitement of a party conference, a ‘Devolution Revolution’. Two, given what we know of local government’s initial positive response to the Government’s devo agenda and that the door seems definitely still open, I’d suggest Catherine’s early optimism has certainly not yet proved entirely misplaced.

Chris Game is a Visiting Lecturer at INLOGOV interested in the politics of local government; local elections, electoral reform and other electoral behaviour; party politics; political leadership and management; member-officer relations; central-local relations; use of consumer and opinion research in local government; the modernisation agenda and the implementation of executive local government.
 Steve Rolfe is a Research Fellow at the University of Stirling. His research interests include community participation and empowerment, social enterprise and housing. Before entering academia, he worked in local government for 15 years in a range of community development and policy roles.
Steve Rolfe is a Research Fellow at the University of Stirling. His research interests include community participation and empowerment, social enterprise and housing. Before entering academia, he worked in local government for 15 years in a range of community development and policy roles.
